INTRODUCTION
Styrene, an organic compound with the chemical formula C8H8, is the precursor of polystyrene and is primarily produced via the catalytic dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene. Approximately 35 million tons of styrene were produced in 2018, with increasing amounts synthesized annually to manufacture products such as plastic, fiberglass, automobile parts, and food containers. Thus, human exposure to styrene could occur in occupational and residential settings and via food intake. Styrene is metabolized to styrene-7,8-oxide by cytochrome P450 2E1 in the human liver (Guengerich et al., 1991). Both styrene and styrene-7,8-oxide are considered toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic. In particular, styrene exhibits neurotoxic properties, and exposure to styrene has been correlated with dysfunctions of sensory organs, such as disorders of vision or hearing (Möller et al., 1990; Gong et al., 2002; Corsi et al., 2007; Gopal et al., 2011; Sliwinska-Kowalska et al., 2020).
Several environmental chemicals exhibit reproductive toxicity in mammalian testes (Akingbemi et al., 2004; Chung et al., 2007; Chung et al., 2011; Traore et al., 2016). Toxicological targets in the testis include germ cells, Sertoli cells, Leydig cells, or all these cells. Among these cell types, Leydig cells, located in the interstitial compartment between seminiferous tubules, produce testosterone, which is critically important for maintaining male homeostasis and reproduction (i.e., spermatogenesis) (Zirkin, 1998). Therefore, potential cellular damage mediated via a specific environmental toxicant could result in Leydig cell death, thereby hindering sperm production (Chung et al., 2011). In addition, given that Leydig cells possess a series of steroidogenic machinery (proteins), including steroidogenic acute regulatory proteins, cytochrome P450 side chain cleavage, and 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, the potential dysregulation of these proteins following exposure to environmental chemicals could seriously impact testosterone production and spermatogenesis (Chung et al., 2011; Abdel-Maksoud et al., 2019).
Accordingly, in the present study, we investigated the cytotoxicity mediated by styrene and styrene-7,8-oxide in TM3 testicular Leydig cells in vitro. To evaluate the cytotoxicity at cellular and molecular levels, we examined apoptosis morphologically and measured the altered expression of apoptosis-related proteins after exposure to styrene or styrene-7,8-oxide. The purpose of this study was to determine whether styrene or its metabolite (styrene-7,8-oxide) could potentially impact Leydig cell fate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Styrene and styrene-7,8-oxide were obtained from Tokyo Chemical Industry (Tokyo, Japan). Hoechst 33258, paraformaldehyde, propidium iodide (PI), and Tween-20 were from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Anti-caspase-3 was from Santa Cruz Biotech (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Anti-cleaved caspase-3 was from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA, USA). Anti-XIAP was from Trevigen (Gaithersburg, MD, USA). Anti-rabbit and mouse Ig-conjugated with horseradish peroxidase were obtained from Amersham Pharmacia Biotech (Piscataway, NJ, USA).
TM3 [normal mouse Leydig cell line; American Type Culture Collection (ATCC), MD, USA] cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (Sigma-Aldrich) supplemented with 5% horse serum and 2.5% fetal bovine serum. The cells were incubated in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2, and were exposed to styrene or styrene-7,8-oxide when confluency reached 50%.
The cells were stained in Hoechst 33258 (4 μg/mL) for 30 min at 37°C, fixed for 10 min in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA), and then observed under an Axiophot microscope (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).
Cells were harvested, fixed with 95% ethanol for 24 h, incubated with 0.05 mg/mL PI, and 1 μg/mL RNase A at 37°C for 30 min, and analyzed by flowcytometry, using Epics XL with an analysis software (EXPO32 TM; Beckman Coulter, MI, USA). The cells belonging to sub-G1 population were considered apoptotic cells, and the percentage of each phase of the cell cycle was determined.
Whole-cell lysates were prepared by incubating cell pellets in lysis buffer [30 mM NaCl, 0.5% Triton X-100, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 1 mM Na3VO4, 25 mM NaF, 10 mM Na4P2O7] for 30 min on ice. After the insoluble fractions were removed by centrifugation at 13,000×g at 4°C for 30 min, the supernatants were collected and protein concentration was determined with a BCA protein assay kit (Pierce Biotechnology, Woburn, MA, USA). The same amounts of proteins (~30 μg) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane. The membranes were incubated for 1 h at room temperature (RT) with a primary antibody in Tris-buffered saline containing 0.05% Tween-20 [TBS-T (pH 7.4)] in the presence of 5% nonfat dry milk. After the membranes were washed in TBS-T, secondary antibody reactions were performed with an appropriate source of antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase. The signals were detected with an enhanced chemiluminescence detection kit (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) in the LAS-3000 detector (Fujifilm, Tokyo, Japan). Immunoblotting for β-actin was performed in every experiment as an internal control.
Cells were harvested and then attached on the slide glass by cytospin centrifugation. Cells were fixed with 4% PFA, washed with PBS, and incubated with 0.2% Triton X-100. Then, cells were incubated with the appropriate primary antibody in 1% bovine serum albumin at RT. For secondary antibody reaction, cells were incubated with an appropriate fluorescence-conjugated secondary antibody at RT. For counterstaining of the nucleus, if required, cells were incubated with PI (50 μg/mL) at RT. Finally, cells were mounted and observed under a confocal microscope (LSM510, Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) at the Neuroscience Translational Research Solution Center (Busan, Korea).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
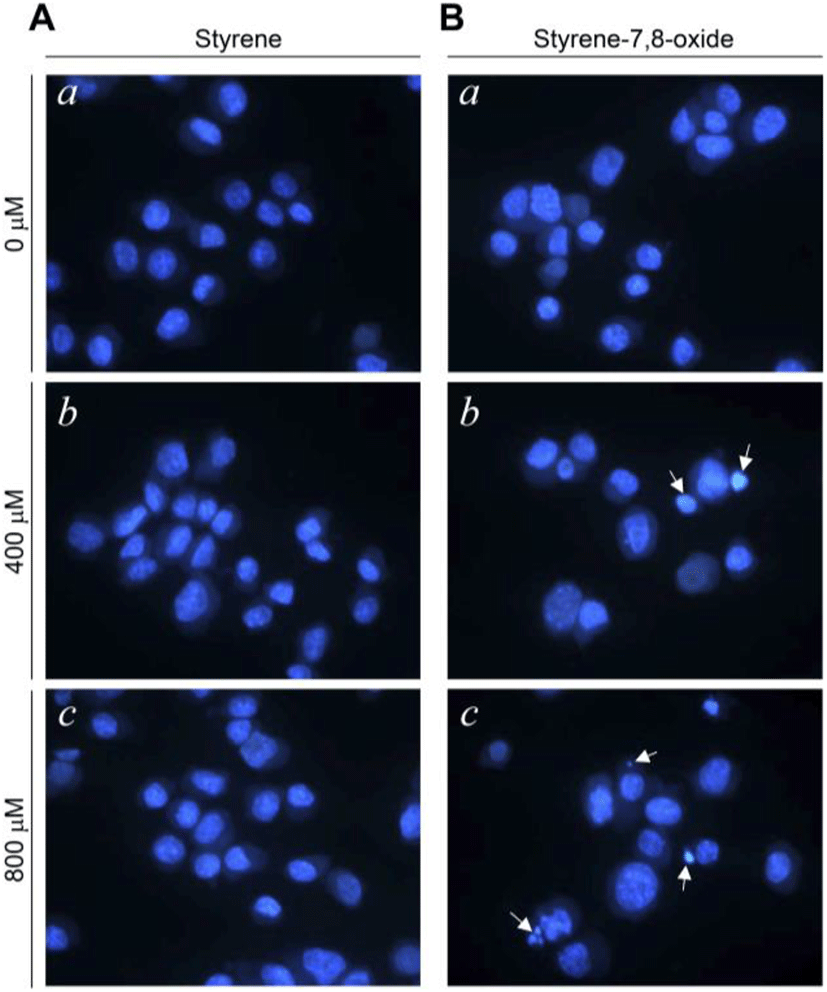
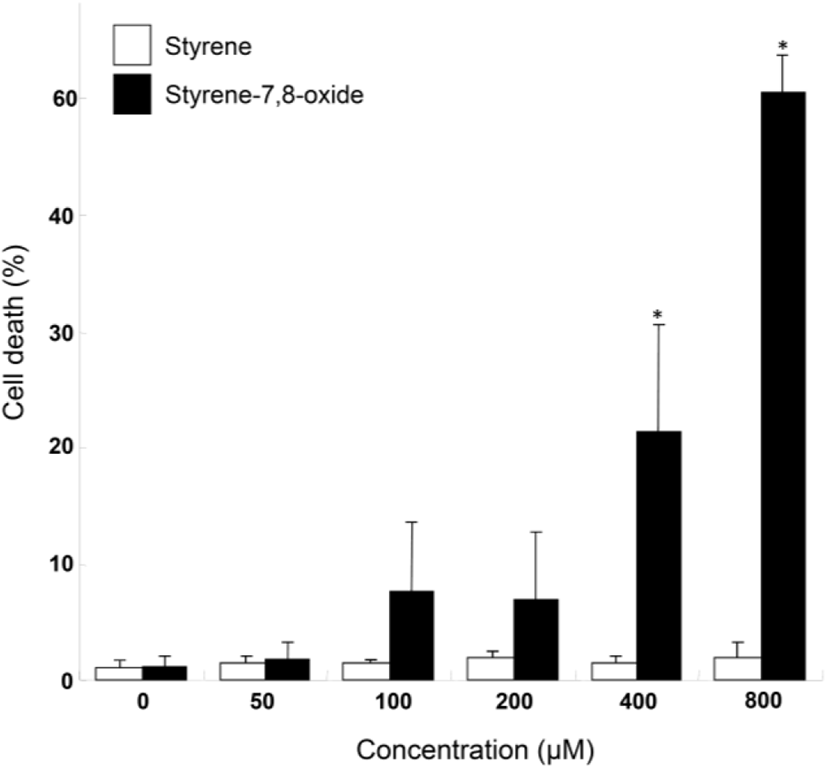
Although styrene cytotoxicity has been tested in several cell types (Cruzan et al., 2002; Corsi et al., 2007), including neuronal cells (Daré et al., 2004; Moujahed et al., 2020), a corresponding investigation has not been performed in testicular cells, particularly Leydig cells. In this study, we first monitored the nuclear fragmentation in Leydig cells after exposure to styrene or styrene-7,8-oxide. Nuclear fragmentation is a well-known morphological hallmark of apoptotic cells (Negri et al., 1996). Surprisingly, Hoechst 33258 cell staining showed that styrene exposure in TM3 Leydig cells did not exhibit nuclear fragmentation at any concentration, even at 800 μM, which is clearly pharmacological (Fig. 1A). In contrast, nuclear fragmentation was seen in styrene-7,8-oxide-exposed cells (Fig. 1B). However, nuclear fragmentation was only observed at higher concentrations (>400 μM) of styrene-7,8-oxide (Fig. 1B). Furthermore, cell death determined by sub-G1 analysis of the cell cycle confirmed that while styrene treatment did not induce significant cell death with any concentration (Fig. 2), styrene-7,8-oxide treatment showed significant cell death numerically at higher concentrations (Fig. 2). These results indicate that cytotoxicity-mediated cell death in Leydig cells is more susceptible to styrene-7,8-oxide than to styrene. Similar results were observed in Leydig cells after exposure to benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) or B(a)P diolepoxide (BPDE) (Chung et al., 2007). These differences in cell death susceptibility may occur because chemicals that retain oxide compounds are more likely able to form DNA adducts, causing DNA damage and cytotoxicity-mediated cell death i.e., apoptosis (Venkatachalam et al., 1993).
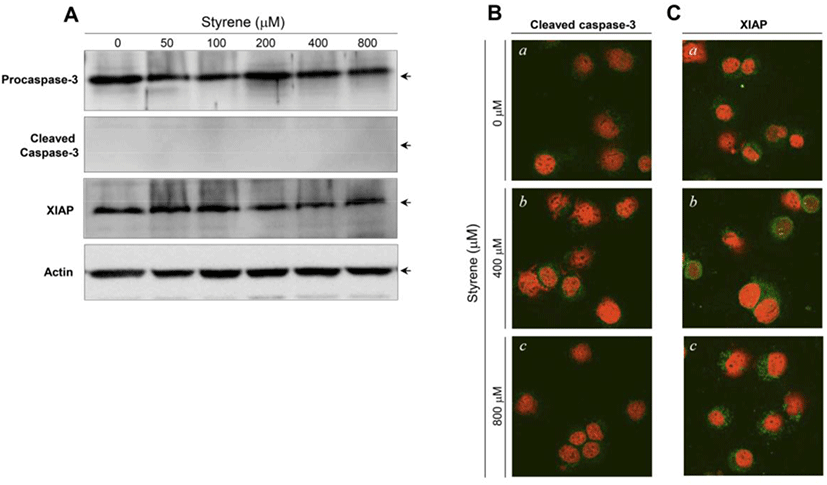
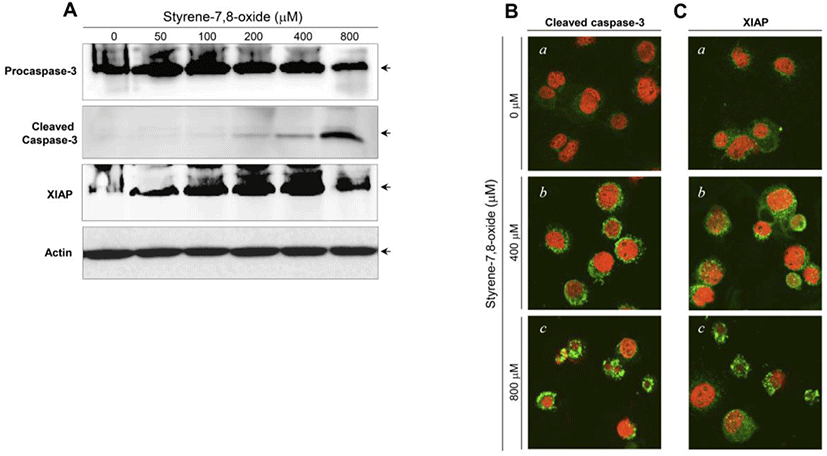
The activation of caspase-3 and upregulation of XIAP have been associated with the induction and suppression of apoptosis, respectively (Porter and Jänicke, 1999; Liston et al., 2003). Following styrene treatment, procaspase-3 and XIAP protein levels did not show significant changes, and cleaved (active) forms of caspase-3 were not detected (Fig. 3A). Consistent with the western blot results, the active forms of caspase-3 and XIAP proteins were not prominently altered in the cytoplasm of cells treated with styrene (Fig. 3B). These results confirmed that apoptosis does not occur after styrene exposure and implied that the cytotoxic effect of styrene on TM3 Leydig cells does not appear be fatal. In contrast to styrene, styrene-7,8-oxide induced cell death in an apoptotic fashion, as seen in caspase-3 activation and increased the expression of XIAP proteins (Fig. 4A). This finding was also confirmed by immunostaining for the active forms of caspase-3 and XIAP (Fig. 4B). These results suggest that TM3 Leydig cells retain an apoptotic mechanism, but the insufficiency or lack of cytochrome P450 enzymes (i.e., CYP 2E1) responsible for the conversion of styrene to styrene-7,8-oxide is the reason why TM3 Leydig cells could be protected from apoptosis induced by styrene exposure.
Taken together, the results obtained in this study demonstrate a fundamental idea that Leydig cells are capable of protecting themselves from cytotoxicity-mediated apoptosis as a result of styrene exposure in vitro. However, styrene exposure in vivo, in experimental animals, is thought to exhibit adverse effects on Leydig cells, because styrene can be metabolized to styrene-7,8-oxide in the liver. It remains unclear whether the steroid-producing function, i.e., steroidogenesis, of Leydig cells is also unaffected by exposure to styrene. We believe that this finding is particularly important now, since polystyrene is a major component of microplastics, which have received increasing attention as an environmental risk factor for human health. Therefore, further studies are needed to elucidate the endocrine disrupting potential of styrene in Leydig cells.







